WHAT IS RNG?
RNG is a pipeline-quality gas that is fully interchangeable with conventional natural gas.1 It is a biogas, the gaseous product created from the decomposition of organic matter, that can be utilized across many applications for organizations to improve their sustainability efforts and reduce their greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
RNG can be produced from numerous sources such as municipal solid waste landfills, digesters at water resource recovery facilities, livestock farms, food production facilities and organic waste management operations.2 According to the RNG Coalition, there are 250 operational RNG facilities across North America, with nearly 240 more planned or under construction. Today, landfill RNG produces 69% of the total RNG supply.3
.png)
HOW IS RNG PRODUCED?
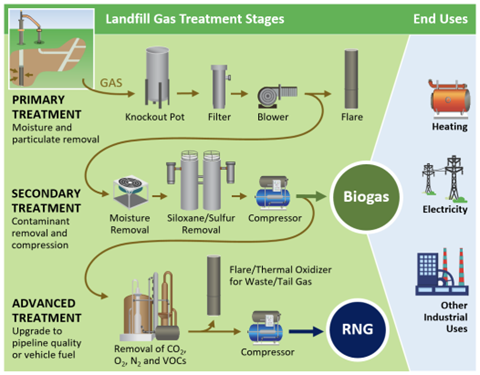
To begin converting biogas, also referred to as biomethane, to RNG, the biogas is captured and purified. Treatment includes removing moisture, carbon dioxide and trace level contaminants such as siloxanes, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hydrogen sulfide. Nitrogen and oxygen content are also reduced during this process. Once upgraded, the gas contains a methane content of 90% or greater. When RNG is injected into a natural gas pipeline, it typically has a methane content between 96% and 98%.
 6
6
WHAT ARE APPLICATIONS FOR RNG?
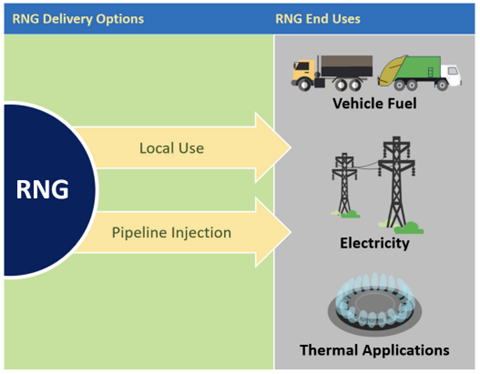
When RNG is produced, it is either injected into a natural gas pipeline or used locally, for example at onsite vehicle fueling stations. Since RNG can leverage existing infrastructure and is so chemically similar to natural gas, RNG is a seamless alternative that can be used either for thermal applications, to generate electricity, as a bio-product feedstock or as a vehicle fuel.
Natural gas powers more than 175,000 vehicles in the United States.4 When biogas is processed to a higher purity standard, the RNG can be used as a transportation fuel in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG) or compressed natural gas (CNG). In addition to the tremendous environmental benefits, using RNG as a transportation fuel also offers economic benefits. RNG qualifies as an advanced biofuel under the Renewable Fuel Standard1 and generates D3 Renewable Identification Numbers (RINs), an environmental attribute that can be marketed to obligated parties.
 6
6
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF RNG
RNG provides many benefits, environmentally and economically.5 For organizations looking to achieve reduced and net-zero emissions, RNG has significantly lower Carbon Intensity scores compared to diesel and can yield GHG emissions reductions of up to 75%.6 Additionally, replacing traditional diesel or gasoline with RNG significantly reduces emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, and contains zero to very low levels of ethane, propane, butane, pentane, or other hydrocarbons. By capturing and transitioning the methane produced at landfills or anaerobic digestion facilities, leveraging RNG mitigates global climate change in the near-term.
HOW TO BEGIN USING RNG
Although RNG production has been accelerating, it is being outpaced by the demand for it. Individuals are putting more emphasis on being environmentally conscious consumers, companies are increasing their focus on ESG initiatives and numerous states are proposing and passing legislation requiring increased use of renewable energy. RNG is an effective pathway for companies to reduce emissions. Since RNG utilizes existing infrastructure and technology, it is a turnkey energy solution. To begin using RNG, it is essential to partner with a vertically-integrated RNG organization that has expertise across the RNG value chain. As a leader in RNG production and end-use delivery, Kinetrex Energy provides unique insight and expertise to help companies quickly transition to RNG, drive sustainability efforts forward near-term and achieve ESG goals.
- https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/natural_gas_renewable.html
- https://www.epa.gov/lmop/renewable-natural-gas
- https://www.rngcoalition.com/
- https://afdc.energy.gov/vehicles/natural_gas.html
- https://www.epa.gov/lmop/renewable-natural-gas
- https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2021-02/documents/lmop_rng_document.pdf
- RNG Facilities Map - https://www.rngcoalition.com/infographic

